How AI Content Moderation Works in Real Time
What are the main benefits of using AI for moderation? What are the principal levels it includes? And why does AI sometimes need to protect users from itself?
AI content moderation keeps community engagement safe by reviewing UGC as it appears. Modern platforms generate far more content than human moderators can process, but AI helps to handle destructive material in milliseconds. How does it work? What type of AI moderation exists, and which problems does it face?
What Is Content Moderation?
Content moderation is the process of reviewing and managing what users post online: text, audio, images, video, etc. The goal is basically to prevent toxic or harmful content from reaching members and altering their experience within the community.
This management can be done manually, with some rule-based exclusions, or fully automated. Usually, it takes a combination of approaches to ensure UGC adheres to a community’s laws and supports a positive overall experience for everyone involved.
That said, content moderation is essential whenever and wherever users interact or actively chat online:
- During sports games (emotions and heated rivalries can easily trigger conflicts)
- In gaming communities (frequent hotspots for trolling or toxic behaviour)
- Trading or investment platforms and communities (high risk of manipulation, misinformation, and scam)
- Movie and TV fandom communities (users can share pirated content)
- Crypto and Web3 communities (targets for phishing, impersonation scams, or wallet-draining links)
- Dating apps and communities dedicated to dating (people are too open, high risk of fraud and harassment)
- Health and wellbeing communities (fragile audience, risky topics)
Why Platforms Now Rely on AI
People respond to the content they consume online by producing even more content. A single active sports chat or livestream thread can generate thousands of messages per minute, across multiple formats. And a significant part of it may prove harmful, misleading, or abusive.
According to Statista, Meta removed 18 million hate-speech posts in Q2 of 2023, and Reddit removed over 780,000 spam subreddits in 2022 alone. Even on LinkedIn, a professional network, over 204,000 pieces of content containing harassment or abuse were removed in the second half of 2022.
At this scale, human moderators simply can’t keep up. Platforms now rely on AI to continuously scan through and prevent harmful material from spreading. And the need grows stronger every year.
Domo’s “Data Never Sleeps” report shows that the number of internet users has grown from 3 billion in 2014 to 5.5 billion in 2024. With billions of people generating and interacting with content daily, the volume is mind-boggling. While keeping it all within the guidelines is paramount, doing so with manual moderation alone is impossible.
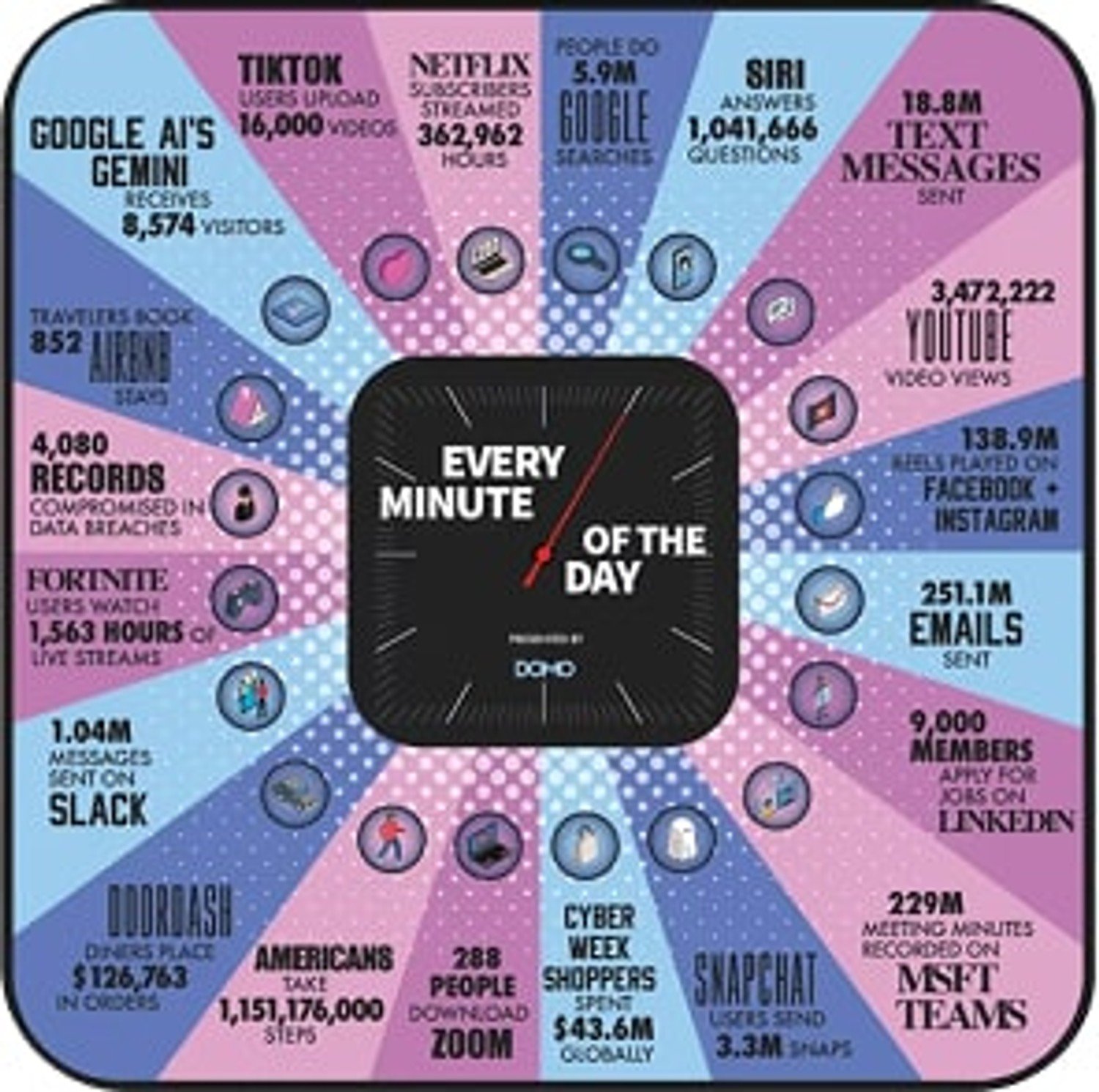
How AI Content Moderation Works
Human moderation takes time and is mentally taxing. The amount of content a person reviews (or the number of people needed in a moderation team) varies depending on the specifics of each platform.
For reference, a TIME investigation revealed that in 2021, Meta contracted more than 15,000 human moderators globally. Many of them were from Sub-Saharan Africa, and their work turned out to be “mental torture.” These moderators had to watch videos showing suicide, child abuse, rapes, and murder, often having as little as 50 seconds to rate the content. Understandably, many of them ended up suffering from anxiety, depression, PTSD, and severe burnout.
So in some instances, not even tens of thousands of moderators can keep up with the volume. And exposing some humans to unlimited trauma just to protect others doesn’t make sense.
To reduce the load on humans, platforms introduced rule-based filtering. More specifically, systems that automatically match content against rigid rules (Eg, “If message contains banned word, block it”).
While these filters helped a bit with text, they barely improved image and video moderation. Even in text, they were easy to evade by switching to coded language (“h@te,” “k1ll,” inside jokes, or emojis). Plus, every new trick required a manual update to the ruleset.
This is the context in which AI content moderation was implemented. Unlike rule-based systems, AI models can interpret context, detect disguised violations, operate in real time, and spare humans from unnecessary exposure to toxic content. Let's dive deeper into the layers which consist of the main AI moderation systems.
The Different Layers of AI Content Moderation
An AI filtering engine can rely on one or several of the following techniques/models:
- Machine Learning Models: ML is the foundation of modern moderation models. It focuses on pattern recognition that models learn through training on large datasets (slurs, harassment patterns, spam behaviour, etc.).
- Natural Language Processing: NLP is a branch of ML that focuses on language. It understands keywords AND tone, slang, or linguistic nuances behind words. And it’s used to detect direct insults, harassment, harmful phrasing, etc.
- Large Language Models: LLMs sit on top of NLP and tackle full sentences or even long conversations at once. By detecting contextual intent, an LLM rates content while acknowledging the sarcasm, veiled threats, or coded hate language.
- Computer vision: This is another branch of ML that focuses on analysing pixels or frames to detect nudity, violence, weapons, hate symbols, deepfake cues, manipulated media, and so on.
And through it all, scoring models and thresholds guide the final decisions. What does this mean?
Instead of a simple label, AI uses classification models to generate a probability score and determine where it falls within predefined thresholds. Depending on the score and threshold, it will take a specific action.
For context:
The score is a number between 0 and 1 that shows how likely it is for a message to be harmful.
The classification models that help determine these scores are AI systems that were trained on millions of human-labelled examples.
E.g.:
- Google’s Perspective API (widely used toxicity scoring model)
- OpenAI’s Moderation Models (classify sexual, hateful, violent, self-harm, and illegal content)
The thresholds are defined by each platform, but typically reflect common industry practice:
- less than 0.4 — content is allowed to be publish instantly
- between 0.4 and 0.85 — can be offensive, therefore sending for human review
- over 0.85 — high-risky, blocking instantly
AI Content Moderation Examples
Now, let’s go a bit deeper into the types of user-generated content that AI moderates.
Text Moderation (NLP)
NLP analyses the sense of individual words and the nuances of human language. Because of that, it thrives where rule-based filtering fails. Also, it’s fast and can be used for real-time detection, especially in chats and comment moderation on social media.

NLP is also widely used in large-scale systems. Meta, for instance, applies NLP across Facebook and Instagram to detect hate speech, bullying, and coded words. On Messenger, it offers built-in NLP through Wit.ai.
Businesses can enable it on their Facebook Pages to automatically interpret incoming messages, extract meaning (like dates or location), and identify user intent.
In gaming chats, disguised insults like “ur tr@sh” (you’re trash) or self-harm encouragements like “kys plz” (kill yourself, please) are so much easier to spot with NLP.
Image and Video Moderation
Computer vision models use machine learning, biometrics, and live analysis to power image and video moderation.
They analyse at the pixel level (images) or frame by frame (videos) to:
- Identify objects and context: Google Cloud’s Vision AI (Cloud Vision API + Video Intelligence API) provides pretrained computer-vision models that can detect explicit nudity, violence, hate symbols, etc.
- Recognise faces: Amazon Rekognition uses face analysis tools to detect faces in images/videos and verify their liveness (to ensure it’s a real person, not a deepfake)
- Read text inside images or videos: Google Cloud Vision API uses optical character recognition (OCR) to spot potential violations embedded in images or video captions.
If NLP takes milliseconds, computer vision takes seconds to process the millions of pixels per image or hundreds of frames per second. Therefore, it’s considered near-real-time filtering.
This form of filtering is beneficial during live streaming. If a clip contains hate symbols (like a swastika), AI identifies them and flags the content within 2 or 3 seconds.
Audio and Multimodal Moderation
Audio moderation is a two-step process where artificial intelligence:
- Uses automatic speech recognition (ASR) to turn speech into text
- Examines that text with NLP
This way, it detects hate speech, threats, and other forms of harassment in voice messages. But audio notes are just one type of user-generated content. Video, for instance, requires audio screening along with other forms of moderation, and that’s when the process becomes multimodal.
Multimodal moderation means the system analyses all the different types of data together, catching violations that single-mode models cannot detect.
If a video shows a harmless scene with an audio threat, a single-mode visual model would most likely approve it. It takes a multimodal model to catch this violation.
YouTube is one of the major platforms that uses multimodal AI for safety. According to their recent blog post, the company uses this technology to reduce the amount of harmful content that 20,000+ human reviewers are exposed to.
Human-in-the-Loop Moderation
When the system can’t decide on an individual case and sends it to a human moderator, we call it human-in-the-loop. It’s a hybrid approach where AI handles the bulk and humans handle cases that require nuance and cultural understanding.
This is an extra, final layer that can be added to all the other forms of AI content moderation.
Think about a livestream where someone makes a borderline racial joke. The system might detect it as a potential violation. Still, if the confidence score falls in the middle range, between 0.4 and 0.85 (because it’s not that obvious), a human will be asked to make the final decision.
Types of AI Content Moderation
We’ve seen which types of content AI moderates and how it does so. Let’s look at when moderation occurs throughout the UGC cycle and what the implications are at each stage.
Pre-Moderation
This one happens before publication. Content is moderated and, if validated as safe, will appear on the platform. If not, it can be blocked, or the user will be notified and given a chance to correct it before publication.
Pre-moderation is the safest option because it almost eliminates the risk of inappropriate content affecting the community. But it also slows down the publishing experience, making users less inclined to contribute.
You’ll notice it’s commonly used on platforms for vulnerable audiences. For instance, YouTube Kids pre-screens uploads before they appear in the app, and Roblox enforces pre-publication filtering for players under 13 (it hasn't been so helpful for them, though). But also on legal-risk audiences (media sites, government portals, and marketplaces like Amazon or eBay that must verify images and descriptions, etc.).
Post-Moderation
Post-moderation comes right after content is published and is the standard choice for chats. Social feeds, live stream discussions, and fast-moving comment sections can also employ it.
Once the AI detects inappropriate content, it can warn the creator, remove the message, prevent the user from posting again, or even send the case to a human moderator. It all depends on the platform rules.
With instant posting, members enjoy the experience more, but that means it’s more likely for toxic content to be visible, even if only for a short time. The risks vary depending on how quickly the engine will detect and handle violations.
Reactive Moderation
With this type of moderation, platforms only review the content that users complain about. It’s an even slower process, and if no one complains, nothing gets reviewed, flagged, or banned. This is common on social media channels, community forums, or even marketplaces like eBay, Amazon, or Airbnb.
On the plus side, reactivity reduces the load on moderators. Still, some members can abuse the report button, and results depend heavily on the community’s level of engagement.
Distributed Moderation
Distributed moderation is when the community moderates its own content at scale. Members collectively score or vote on content, and the system displays the aggregated results. Based on votes/scores, the platform can hide, collapse, demote, or even remove content.

One of the most popular examples is the voting system on Reddit, where users can upvote or downvote posts and comments. Low-quality or harmful messages are hidden or collapsed.
Hybrid Moderation
The most common model, hybrid moderation, combines AI, human surveillance, and automated rule-based filtering. The larger the community, the greater the need for hybrid moderation to address challenges and ensure a safe environment.
Typically, in these settings, rule filters and AI handle routine, high-volume moderation, making decisions on spam filtering, toxicity scores, or NSFW ratings. Whatever seems ambiguous (context-dependent, edge cases, appeals) is sent to human moderators.
This approach allows platforms to balance accuracy with scalability. Harmful content is detected as fast as possible, regardless of how much content members generate. And where nuance truly matters, humans take the shots.
Key Challenges in the Generative AI Era
Salesforce research revealed that:
- 49% of people have used generative AI
- 65% of users are either Millennials or Gen Zers
- 70% of Gen Zers say they use and increasingly trust this technology
Clara Shih, CEO of Salesforce AI, says, “In my career, I’ve never seen a technology get adopted this fast.”
That said, it’s getting harder and harder to tell which is human- and which is AI-generated content. And companies that develop Gen AI tools are aware of challenges and do their best to mitigate the risks.
Take Synthesia, one of the leading AI video-generation platforms. Their technology creates digital versions of real humans and uses them to generate full videos from plain text in a matter of seconds.
The company enforces stringent safeguards around avatar creation and the use of these videos. They proactively stress test their systems under rigorous, independent read-team evaluations. And they’re highly invested in preventing deepfakes and damaging content from slipping through.
With this context, let’s take a closer look at the main challenges of content filtering in the gen AI era.
Harmful AI-Generated Content
AI is trained on human-made content. By definition, its whole purpose is to be as realistic as possible. Plus, when someone uses AI content to harm, they’ll intentionally design it to bypass filters.
All these factors, combined with the volume and speed at which AI content is created, make it increasingly more complex to detect such instances. Hence, the growing number of resources designed to teach us how to tell what’s real and what's not.
Over- and Under-Enforcement
Over-enforcement occurs when a system has too strict thresholds or misinterprets sarcasm and harmless mentions as harmful. Wrongfully-sanctioned members become frustrated with their experience and may choose to step back (low engagement) or even step away from the community (high churn).
Under-enforcement occurs when a system frequently fails to detect high-quality harmful AI-generated content, coded words, and subtle threats, and under-blocks violations.
Members are exposed to this content, the platform suffers reputational damage and, in more serious cases, even legal risks.
None of these is desirable, and systems have to carefully balance their scores and thresholds to avoid model errors.
Missing Context
Imagine being banned from a gaming community for writing in the chat, “I’m gonna destroy you tonight.” That’s friendly banter that AI may not interpret as such, depending on the context it has. Often, factors like irony, sarcasm, cultural references, or in-jokes can make it harder to evaluate content in its broader context. Without deeper contextual queues, AI moderation systems can easily misinterpret intent and either miss violations or flag non-existent ones.
Language Gaps
The less familiar a language is, the less training data that the model will have, and the less reliable its output will be. When content includes terms from languages like Maori, Welsh, Icelandic, or Basque, AI can wrongly flag as dangerous even the most harmless idioms or common expressions of those languages. All because the model doesn’t understand the nuance, since it hasn’t been trained on data that included it.
Benefits of AI Content Moderation
Paradoxically, AI is both part of the problem and part of the solution to moderation challenges. The benefits of automating processes with artificial intelligence are vast and powerful.
For starters, AI gives speed and scalability to any moderation system. Since the system operates on clear rules, it’s more likely to return more accurate results (as opposed to human moderators, who might interpret the same rule differently depending on who’s reviewing).
Also, with AI doing the heavy lifting and handling most moderation, humans are under less pressure. They have more bandwidth and mental clarity to interpret the fewer but more challenging situations that the AI sends in for revision.
Once a system is implemented, costs become more predictive, and the process finds its groove. With faster, more reliable moderation, users have an improved experience, which will directly impact community engagement.
DAU and retention naturally increase because members feel safe sharing and consuming content within the community.
UGC is an ecosystem that expands at lightning speed. In this ecosystem, AI moderation serves as the foundation that enables communities to scale in the safest possible ways.
Best Practices for AI Moderation
Success depends on whether you use a hybrid moderation system, how thoroughly you log decisions, and how often you audit and refine your system.
The following best practices will help you get there.
Measuring and Tuning AI Moderation Quality
Set-it-and-forget-it doesn’t apply to moderating with AI tools. You can’t let a system flag content without looking at how often it’s right (precision) and how much toxic content it correctly flags (recall). Or whether it scores false positives/negatives (over- or under-enforces).
Error analysis and threshold tuning are critical steps for improving the process.
Policy Design, Appeals, Compliance, and Governance
The moderation policy, along with the violation categories, is the bedrock. You must clearly define:
- What counts as a violation
- What severity levels will the system use to categorise violations
- What are the threshold rules (when to allow, escalate, or block)
- How should the system proceed finding a threshold
Any content decision has to be handled within a transparent appeal process. Moderating content involves operating with user data, which carries many legal responsibilities. The platform owner has to deal not just with building trust and transparency, but follow the regulations:
- GDPR privacy laws (data privacy and user consent)
- Online platform regulations, such as the EU Digital Services Act (platform accountability and risk mitigation)
- Safety requirements under the UK Online Safety Act (proactive detection and removal of illegal content)
The Future of AI Moderation
With Gen AI pervading online, moderation must focus on developing increasingly more complex and performative models that are:
- Multimodal: can evaluate various types of content simultaneously.
- Context-aware: can understand the whole picture, not simply isolated elements, by examining an intent history, considering cultural nuances, and situational clues.
- Agent-based: uses AI agents that can detect violations and act in real time.
- Cross-contextual: notice the safety signals and share them across digital platforms, preventing repeated violations.
Build Safer In-App Communities with Watchers
If you plan to build communities in-app, you need to protect your users. We offer community chats which are not only engaging but safe and trustful. We build 4-layer AI moderation system and constantly develop and improve it. Learn more and get to know how to build safe space for users, book a call with our team.
FAQs About AI Moderation
What is AI moderation?
It’s an automated process of reviewing and managing UGC by leveraging ML, NLP, and computer vision. AI moderation detects in real time content that’s harmful or violates policies and can block it directly or dispatch it for human moderation.
How accurate is AI moderation?
Moderating with AI is highly accurate, although results vary by use case and false positives/negatives still occur (especially with nuanced content). Modern systems keep humans in the loop for ambiguous contexts or high-stakes decisions.
What are the problems with AI moderation?
- Challenges in comprehending nuances that leads to false positive or false negative decisions)
- Limited adaptability to slang, memes, and other conversations linguistics elements
- Weaker performance with rarer languages and dialects
- Difficulties in detecting evasion tactics, such as intentional misspellings
- Limited ability to indentify with deepfakes
- Reasons can be unclear
Is AI moderation better than human moderation?
Rather than “better”, AI screening is faster and more scalable. While AI can cover a significantly higher volume of content in real time, it can’t do it all, and it still relies on human review for the less clear contexts. In practice, the best results come from combining AI with human moderation.
References
- Social media content moderation and removal - statistics & facts | Statista
- Data Never Sleeps 12.0 | Domo
- Inside Facebook’s African Sweatshop | TIME
- Five machine learning types to know | IBM
- What is natural language processing (NLP)? | Tech Target
- What is computer vision? | Azure Microsoft
- Perspective API | Perspectiveapi.com
- Open AI Platform - Moderation | OpenAI
- Use of Natural Language Processing in Social Media Text Analysis | Research Gate
- Natural Language Processing for Messenger Platform | Facebook
- Build Natural Language Experiences | Wit.ai
- Vision AI | Google Cloud
- Amazon Rekognition | Amazon
- Our Approach To Responsible AI Innovation | Inside YouTube
- Synthesia’s Content Moderation Systems Withstand Rigorous NIST, Humane Intelligence Red Team Test | Synthesia Blog
- Fact check: How to spot AI-generated newscast | DCNews
Boost your platform with
Watchers embedded tools for ultimate engagement
